I often have the honor of working with parents for many years, from birth through age 9. The topics we focus on change as the children get older.
- When the children are babies, we focus on creating an environment for learning, serve and return and the relationships that we form through that responsive play.
- With toddlers, we talk about emotional literacy and tantrums
- For preschoolers, we address discipline, and how to balance setting limits for safety versus letting them explore their world
- This post is focused on elementary age children and questions to reflect on how parenting is different at this age. But first, let’s look at a theoretical approach to the different stages of parenting.
Stages of Parenting
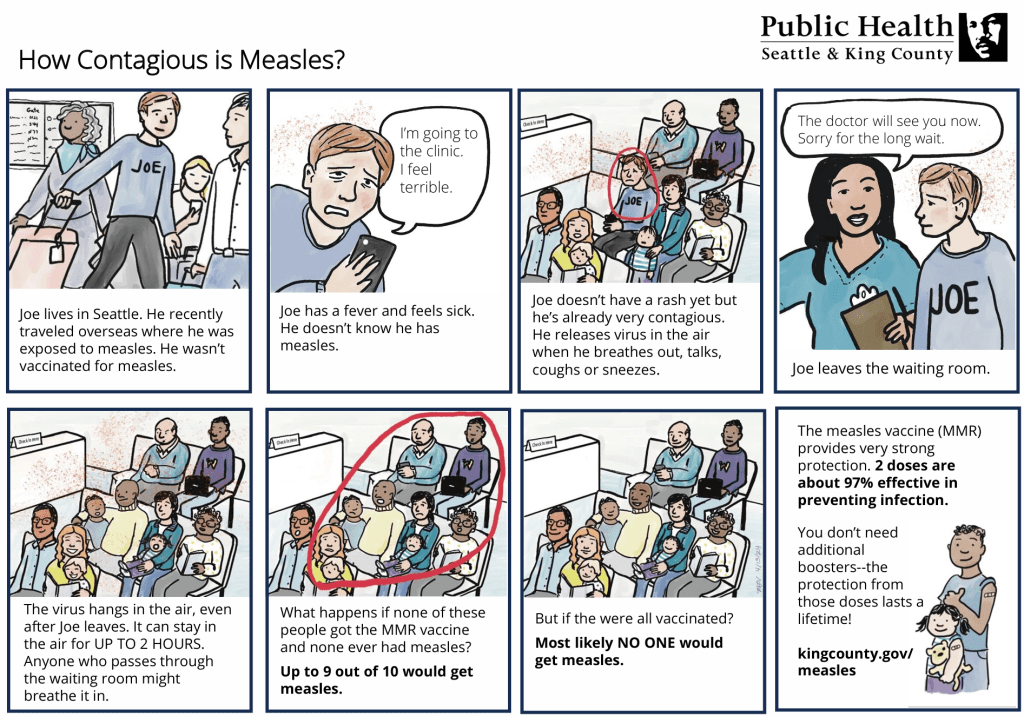
Researcher Ellen Galinsky interviewed 228 parents (of 396 children) with diverse parenting experiences. She found common threads showing six distinct stages of parenting.
Stage One: Image-Making
Before the first baby is born, parents begin to create pictures in their minds of what parenting will be like and what kind of parent they hope to be. They began to adapt their home and their lifestyle to accommodate the child. They observe other parents and reflect on how they were parented to help create their self-image as a parent.
Stage Two: Nurturing
From birth through the first two years. Focused on physical care, soothing, snuggling, and playing. The main goal is to develop a relationship with their child. As the attachmentgrows, parents evaluate their priorities for how much time to spend with the baby versus other aspects of life, including other relationships, and how much of their identity is being a parent.
Stage Three: Authority
From about age 2 to age 5. Parents are more certain of their own identity as parents and of their relationship to their child. They begin to define the family’s rules, decide how strictly to enforce rules and what to do when rules are broken. The main task is deciding how much authority to exert over the child’s behavior versus how much freedom to allow.
Stage Four: Interpretive
The elementary school years. Parents evaluate their own strengths and challenges, and also evaluate their child in comparison to others and to their expectations. The main task is interpreting the child’s experiences as they are increasingly exposed to a world outside their family. Parents answer questions, and determine what behaviors and values to teach. They decide how and where the child spends time and with whom. They decide how involved to be, and when to make the decisions versus when to let a child make choices independently.
Stage Five: Interdependent
In the adolescent years, parents redefine their authority and renegotiate the relationship with their child, who is increasingly making decisions independently, out of the parent’s view. Parents need to trust that they have instilled good values in the child. They don’t allow their adolescent to have complete autonomy, but do allow for more discussion about rules.
Stage Six: Departure
As the child reaches adulthood, parents prepare for the departure, re-evaluate their parenting accomplishments and failures, and re-define their parenting identity and relationships. Parenting becomes less central to their identity and their daily lives.
Parenting in the Interpretive Stage
School and peer relationships assume the central role in the child’s life, and start pulling attention and energy away from the family unit. Parents have much less time with their children than before so need to be more focused on their goals for that time.
Here are decisions parents are making during their child’s elementary school years, as they realize the increasing separation between their identity and the child’s identity.
- What kind of life do I want to provide? (And what can I afford to provide?) What do I say yes to in terms of new clothes or toys, and activities to do. What do I say no to? How do I manage the inevitable times when my child says “that’s not fair! All the other parents let their kids _____.”
- How should I interpret the world for my child? For example, if they ask questions about race, death, sex, religion, and so on. How do I share my beliefs and values with them to give them an internal compass? (There are resources on how to talk about difficult topics at https://gooddayswithkids.com/better-you-than-youtube/)
- How do I want my child to behave? (And have good behavior internalized as self discipline?)
- What do I want them to be capable of and responsible for? (e.g. chores, practicing and playing an instrument or a sport) What new privileges / responsibilities will I introduce (for example: allowance, a phone, going places independently.)
- How involved do I want to be involved in their life, at home and away from home?
- When should I step in to help, and when should I back off and let them make decisions and try things independently?
- How do I support homework?
- How do I ensure they have the skills and knowledge to self-manage healthy habits like good nutrition, personal hygiene, and good sleep?
- How involved do I want to be with the other significant people in their lives. (Friends, parents of friends, teachers, counselors, sports coaches…)
- How do I support them when they’re navigating the emotional ups and downs of peer relationships? How do you monitor friendships while not overly interfering?
- How do I hope to define our changing relationship? For example: how much do we hug, hold and cuddle as they get older? How involved are we in bedtime and morning routines? What do we do together for fun and connection?
- When they are adults, how do I want them to look back on this time? How am I hoping they’ll remember what kind of parent I was?
A helpful resource for child development milestones for these years, and how to support your child’s growth and learning is: https://childdevelopmentinfo.com/ages-stages/school-age-children-development-parenting-tips/